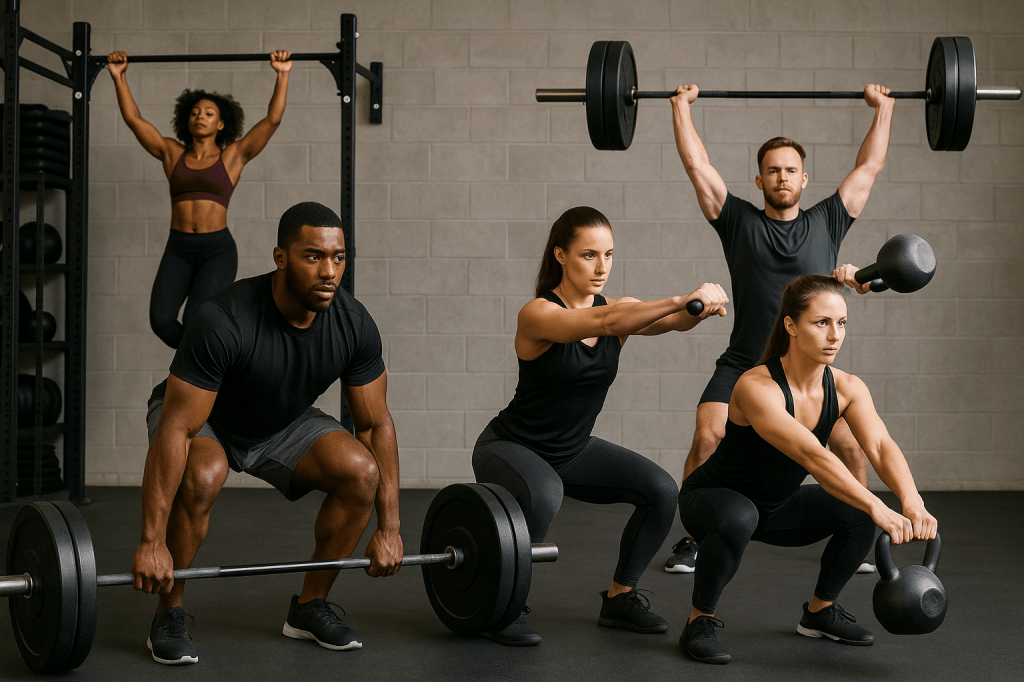
When it comes to building muscle and enhancing athletic performance, compound exercises are the cornerstone of effective strength training. Unlike isolation moves that target a single muscle, compound exercises engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making them a time-efficient and powerful way for athletes to increase strength, improve fitness, and reduce injury risk.
Why Compound Exercises Matter for Athletes
Athletes rely on functional strength — the ability to perform movements that mimic real-world activities or their specific sport. Compound exercises perfectly align with this goal because they replicate multi-joint motions, promote muscle coordination, and boost overall power.
By incorporating compound lifts into your training routine, you stimulate greater muscle activation, leading to improved muscle growth and strength gains. Additionally, these exercises enhance core stability and joint health, essential for athletic longevity.
Top Compound Exercises for Muscle Building and Athletic Fitness
Here are some foundational compound exercises every athlete should consider, along with step-by-step instructions to perform them safely and effectively:
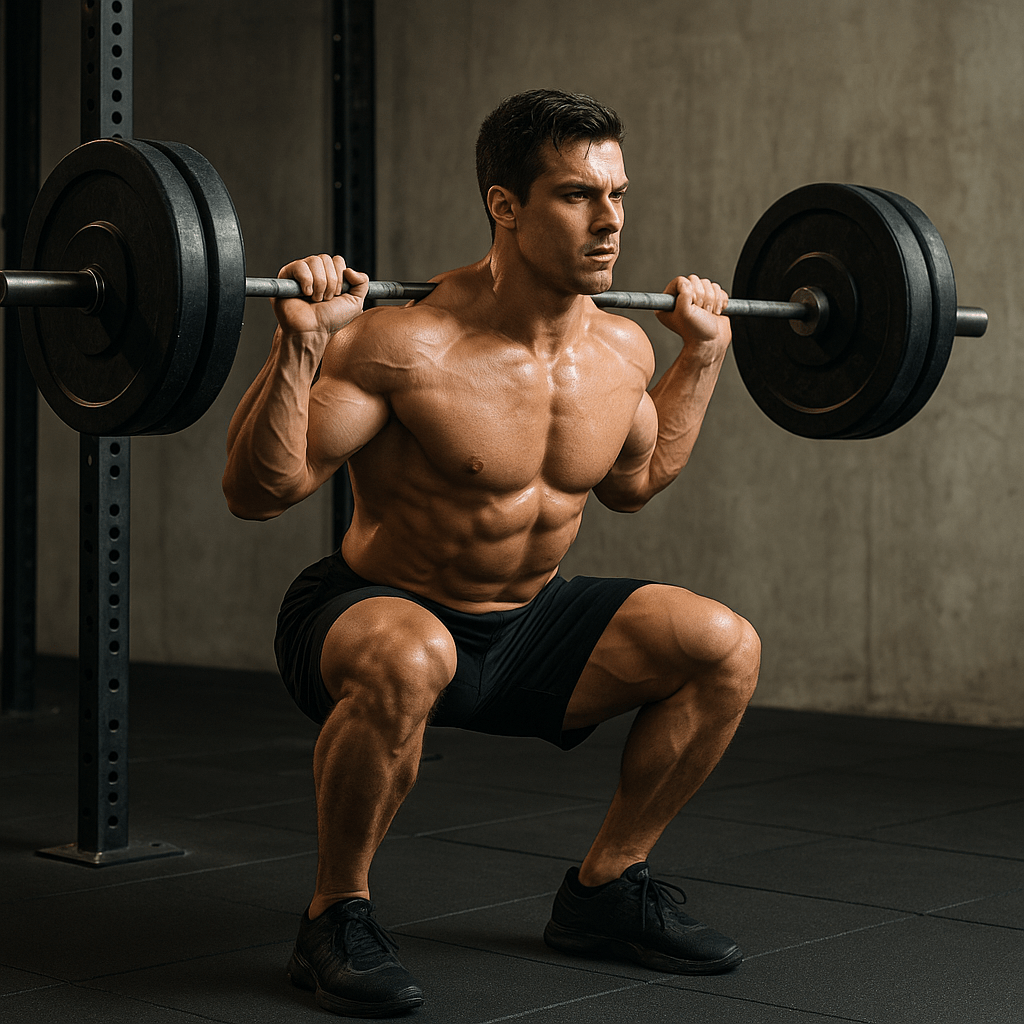
- Squats
Targets: Quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, core, and stabilizing muscles.
How to Perform a Squat:
Place your feet roughly between hip and shoulder width, allowing your toes to angle outward slightly.
Engage your core and keep your chest up.
Gradually lower yourself by bending at the hips and knees, as though you’re lowering into a seated position.
Lower yourself until your thighs are roughly parallel to the floor, or as far as your flexibility comfortably permits.
Drive upward by pressing firmly through your heels to rise back to the starting stance.
Make sure your knees stay aligned with your toes during the entire motion.
- Deadlifts
Targets: Hamstrings, glutes, lower back, traps, and grip.
How to Perform a Deadlift:
Set your feet about hip-width apart and position the barbell just in front of your shins.
Hinge at your hips and bend your knees to grasp the bar with hands just outside your knees.
Tighten your core muscles, maintain a straight back, and keep your chest upright.
Drive upward by pushing firmly through your heels, extending your hips and knees while keeping the barbell close to your body during the lift.
Once fully upright, begin lowering the bar by first hinging at your hips, followed by bending your knees in a controlled manner.
- Bench Press
Targets: Chest, shoulders, triceps.
How to Perform a Bench Press:
Position yourself flat on the bench with your feet planted solidly on the ground for stability.
Grip the bar with your hands placed slightly wider than shoulder distance.
Carefully lift the bar off the rack and begin lowering it in a controlled motion toward the center of your chest.
As you lower the bar, keep your elbows angled roughly 45 degrees away from your body.
Press the bar upward until your arms are extended, keeping the motion steady and controlled.
Avoid snapping your elbows straight; instead, stop just short of full lockout to maintain muscle tension.
- Pull-Ups and Chin-Ups
Targets: Upper back, biceps, grip strength.
How to Perform a Pull-Up:
Grab the pull-up bar with your palms facing away for a pull-up or toward you for a chin-up, placing your hands roughly shoulder-width apart.
Hang with your arms fully extended.
Activate your upper back muscles and begin pulling yourself upward by bending your elbows, aiming to bring your chest close to the bar.
Perform the movement with control, avoiding any swinging or using momentum to assist.
Lower yourself down slowly and with control until your arms are fully extended.
Overhead Press
Muscle Groups Worked: Shoulders, triceps, upper chest.
How to Perform the Overhead Press:
Position your feet about shoulder-width apart and hold a barbell or dumbbells at shoulder level, keeping your palms facing forward.
Tighten your core muscles and maintain a neutral, straight spine throughout the movement.
Raise the weight above your head until your arms are fully extended.
Avoid arching your back; keep your ribs down and core tight.
Slowly lower the weight back to shoulder height.
Tips for Effective Strength Training with Compound Movements
Focus on Form First: Proper technique is critical. Begin with lighter loads to perfect your technique before increasing the weight.
Progressive Overload: Gradually increase weights or reps to continuously challenge muscles and stimulate growth.
Balanced Routine: Incorporate compound exercises targeting all major muscle groups to avoid imbalances and reduce injury risk.
Adequate Recovery: Strength training is intense; allow muscles time to repair and grow with rest days and proper nutrition.
The Benefits Beyond Muscle Growth
Compound exercises do more than build muscle. For athletes, they:
Enhance coordination and balance by requiring multiple muscles and joints to work together.
Improve cardiovascular fitness due to their demand on large muscle groups.
Support functional movement patterns, making athletic performance more efficient and powerful.
Reduce injury risk through strengthened muscles and improved joint stability.
Incorporating compound exercises into your strength training routine is a proven way to build muscle and elevate your athletic fitness. By focusing on these foundational movements and following smart training principles, you can unlock your full potential and enjoy the benefits of enhanced strength, performance, and overall wellness.